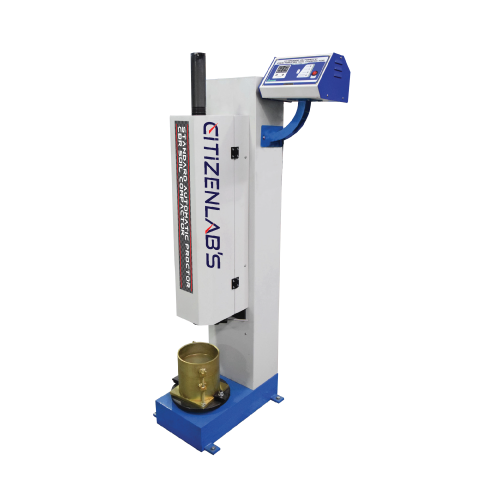
Description
Standard: SANS 3001-GR31 : 2010
CBR / MOD Compaction
The Automatic CBR/MOD Compaction Hammer is designed to provide a uniform compaction of specified effort, thus ensuring repeatable test results and eliminating any operator fatigue during the tests.
The unique design is to allow the hammer to drop at the required height (305 and 460 mm) onto the specimen that also rotates the mould circularly to distribute the blows uniformly over the surface of the specimen. The robust steel frame design housing the motors with durable gearboxes and lifting mechanism which assure uniformity of drop height at all specimen levels. The compactor is provided with a 2.500 kg and 4.500 kg hammer.
Technical Specifications
| Model Number | 5025 X / SAS |
| Blow Rate | 50 – 60 blows / min |
| Adjustable Rammer Weight | 2.5 kg / 4.5 kg |
| Adjustable Drop Height | 305 mm or 460 mm |
| Product Dimension (mm) | 490 (L) x 360 (W) x 1370 (H) |
| Packing Dimension (mm) | 590 (L) x 460 (W) x 1570 (H) |
| Approx. Product Weight | 150 kg |
| Approx. Packing W | 180 kg |
| Power | 220 ~ 240 V, 250 W, 8 A, 1 Ph, 50/60 Hz |
Unit Consist Of:
| Model Number | Parts Description | Qty |
| 5025 X / SAS – P 001 | Digimatic Control Unit | 1no. |
| 5025 X / SAS – P 004 | Ø50mm Lifting Rammer c/w Counter Weight | 1set. |
Optional Accessories
| Model Number | Accessories Description |
| 5025 X / 005 – A 001 | Soundproof Security Cabinet |
Test Procedure of Proctor CBR Soil Compactors
-
Sample Preparation:
- Collect representative soil samples from the site.
- Air-dry the samples and break up any aggregates.
- Sieve the soil to remove any large particles or debris.
-
Determination of Moisture Content:
- Take a portion of the prepared soil sample and determine its initial moisture content using an appropriate method, such as ASTM D558 or AASHTO T134.
-
Compaction Test:
- Set up the Proctor/CBR Soil Compactor according to the manufacturer’s instructions and calibrate it if necessary.
- Place a specified amount of soil into a standard compaction mold (usually a cylindrical mold with known dimensions).
- Determine the compaction effort required based on the type of Proctor test being conducted (Standard Proctor or Modified Proctor).
- Compact the soil in layers by applying a specified number of blows from the compaction hammer. The blows are evenly distributed over the surface of each layer.
- Measure and record the height of each compacted layer.
- Repeat the compaction process for additional soil samples at varying moisture contents.
-
Determination of Dry Density:
- After compacting all the samples, carefully extract them from the molds.
- Determine the dry weight of each compacted sample by oven-drying them to remove all moisture (ASTM D558 or AASHTO T134).
- Calculate the dry density (bulk density) of each sample using the known volume of the mold and the dry weight of the soil.
-
Plotting the Compaction Curve:
- Plot a graph of dry density versus moisture content for the tested soil samples.
- Identify the maximum dry density and the corresponding optimum moisture content from the curve.
-
Interpretation:
- Evaluate the results to determine the suitability of the soil for engineering applications, such as road construction or foundation design.
- The maximum dry density and optimum moisture content provide crucial information for achieving the desired level of compaction in the field.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.